Blog # 26
Radiation, Electric & Magnetic Fields
I own Samsung Galaxy and found the following legal information on my cell phone:
Read this information before using your mobile device.
- Section 4: Health & Safety Information
This section outlines important safety precautions associated with using your device. The terms “mobile device” or “cell phone” are used in this section to refer to your device. Read this information before using your mobile device.
For specific provisions or legal information relating to your device, please refer to the printed Terms & Conditions included with your device, or visit www.samsung.com and use the model number to locate the product support page.
Caution! To avoid electric shock and damage to your device, do not charge device while it is wet or in an area where it could get wet. Do not handle device, charger or cords with wet hands while charging - Exposure to Radio Frequency (RF) Signals
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has published information for consumers relating to Radio Frequency (RF) exposure from wireless phones. The FDA publication includes the following information:
Do cell phones pose a health hazard?
Many people are concerned that cell phone radiation will cause cancer or other serious health hazards. The weight of scientific evidence has not linked cell phones with any health problems.
Cell phones emit low levels of Radio Frequency (RF) energy. Over the past 15 years, scientists have conducted hundreds of studies looking at the biological effects of the RF energy emitted by cell phones. While some researchers have reported biological changes associated with RF energy, these studies have failed to be replicated. The majority of studies published have failed to show an association between exposure to radio frequency from a cell phone and health problems.
While in use, the low levels of RF energy a cell phones emits are in the microwave frequency range. Exposure to low level RF energy that does not produce heating effects causes no known adverse health effects.
Note: While in stand-by mode, cell phones also emit RF energy at substantially reduced time intervals.
While in use, high levels of RF energy can produce health effects (by heating tissue).
The biological effects of RF energy should not be confused with the effects from other types of electromagnetic energy.
Very high levels of electromagnetic energy, such as is found in X-rays and gamma rays, can ionize biological tissues. Ionization is a process where electrons are stripped away from their normal locations in atoms and molecules. It can permanently damage biological tissues including DNA, the genetic material.
The energy levels associated with radio frequency energy, including both radio waves and microwaves, are not great enough to cause ionization of atoms and molecules. Therefore, RF energy is a type of non-ionizing radiation. Other types of non-ionizing radiation include visible light, infrared radiation (heat), and other forms of electromagnetic radiation with relatively low frequencies.
While RF energy does not ionize particles, large amounts can increase body temperatures and cause tissue damage. Two areas of the body, the eyes and the testes, are particularly vulnerable to RF heating because there is relatively little blood flow in them to carry away excess heat.
New health technologies and medical devices using ionizing radiation have led to major improvements in the diagnosis and treatment of human disease. However, inappropriate or unskilled use of such technologies and devices can lead to unnecessary or unintended exposures and potential health hazards to patients and staff.
The safe use of health technology—from beds and stretchers to large, complex imaging systems—requires identifying
possible sources of danger or difficulty with those technologies and taking steps to minimize the likelihood that adverse
events will occur.
Nurses as health-care providers need to develop skills and self-assurance to feel comfortable
speaking out in situations of uncertainty, regardless of their position in the medical and/or
organizational hierarchy, and the position of the others involved in the situation. Knowing what precautions to take when working around radiation helps keep nurses safe. It’s very important that nurses protect themselves and limit amount of radiation they are exposed to in the workplace. Nurses need to know what radiation they are working with and what the precautions are for that type of radiation. Establishing a radiation safety culture is important. For example, In the OR, nurses working around fluoroscopy machines should wear a lead apron if they are within 1 meter of the patient. The apron should be in good repair, with no tears or missing straps or buckles. The waist-level strap should be placed above the hips to shift the apron’s weight off the shoulders.
Nursing Informatics is a well established specialty within nursing, which today has evolved to be an integral part of healthcare delivery and a differentiating factor in the selection, implementation, and evaluation of health IT that supports safe, high quality, patient-centric care. Together, nurses and nursing
informatics must lead, and be
visible, vocal and present at
the table to achieve healthcare
delivery transformation. Statement which provides background on key related issues and identifies specific recommendations for eliminating barriers and
addressing nursing’s role in transforming healthcare through the use of IT, particularly in regard to the role of nursing informatics could be a good starting point.
NEWS
Cosmetics industry crushes bill that would have made makeup and hair products safer
DAVID LAZARUS, APR 10, 2019
The $70-billion cosmetics industry prevailed over California consumers this week, succeeding in shelving a bill that would ban potentially toxic ingredients from makeup, hair products and other personal-care goods.
The state Assembly’s Environment, Safety and Toxic Materials Committee put off a scheduled vote on the Toxic-Free Cosmetics Act (AB 495) as it became clear to supporters they didn’t have enough votes to move the bill to the Assembly Health Committee, which was to take up the legislation on April 23.
The Toxic-Free Cosmetics Act now likely won’t resurface until next year.
Industry groups fiercely opposed the bill, arguing that there isn’t enough scientific evidence to merit banning certain chemicals, including asbestos and lead, from personal-care products. The California Chamber of Commerce branded the bill a “jobs killer.”
Emily Rusch, executive director of the California Public Interest Research Group, told that she’s disappointed by the industry’s win but not giving up.
“Most people use multiple personal-care products every day — makeup, shampoo, deodorant,” she said. “We need to keep pushing manufacturers to make them safer. They clearly aren’t going to do it on their own.”
With a little searching, you can find hair products that don’t contain parabens, or eye makeup without carbon black. And alternatives don’t necessarily cost more.
Walgreens, Target, CVS and Walmart are among major retailers that already have committed to getting safer cosmetic products onto their shelves.
Module # 25
Greening Healthcare
In other hand, there are many remarkable practices which help to green my workplace such as recycling the waste.
The Green Core is a collective organization that represents its diverse community and works on educating the students about issues revolving around food sustainability and clean & renewable energy systems. The Green Core is dedicated to implementing sustainability at college through empowering students to become leaders in the green movement. Put simply, sustainability requires that the team limit negative impact on the natural, social, and economic environments, while at the same time positively impacting these environments.
- reducing solid waste;
- increasing recycling and reuse (includes not only paper/aluminum/glass/plastic recycling but also how best to share excess supplies/furniture/equipment/machinery internally, etc.);
- increasing composting;
- eliminating toxic output (e.g., eliminating chemical cleansers, etc.);
- reducing water consumption via xeriscaping/native plants, low-flow toilets, etc.;
- reducing energy consumption via the use of alternative energies (solar, alternative fuels, etc.);
- reducing air pollution by encouraging car pooling, use of public transit, etc.;
- utilizing green building standards for new construction and renovations (encouraging the use of renewable resources, etc.);
- educating the students, faculty, and staff with respect to adopting practices that promote sustainability in their everyday lives; and
- educating and training students for environmental careers (green construction, alternative fuels, solar panel installation, green business certification, habitat restoration, etc.).
The Budget Department serves as a leading supplier of accurate, timely and meaningful budget and financial information to management, Board, and other constituencies in order to support resource allocation and decision making.
NEWS
Apr 22, 2019
Kids in Southwestern Pennsylvania are exposed to carcinogenic coke oven emissions at shockingly higher rates than the rest of the country
Blog # 24
Energy & Health
A transition to clean, renewable energy will combat climate change, while also reducing the burden of disease from local pollution and occupational hazards. Reducing energy consumption should be the first step. Access to clean, reliable, and affordable sources of energy is critical to improving health across the globe. Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar require some public health considerations including those related to noise pollution and waste disposal, respectively. However, their overall population health burdens are much lower than for fossil fuel-based sources. Substantial public health co-benefits can be realized with a shift towards clean, renewable energy choices.
I personally can have an important role in transition to clean and renewable energy by educating the public and also playing as a role model and consuming these type of energies.
San Mateo County and the Office of Sustainability offer a range of tools, assistance programs and resources to help everyone in the County work together to use energy wisely and reduce our climate impact.
- The San Mateo County Energy Watch program is a partnership between PG&E and the City/County Association of Governments of San Mateo County.
- Peninsula Clean Energy (PCE) was launched collaboratively by the County of San Mateo and all twenty of its cities to help the environment through cleaner energy, while helping customers save money through lower rates.
- The Bay Area Regional Energy Network (BayREN) is a collaboration of the 9 Bay Area Counties to promote healthy, efficient buildings. The BayREN offers rebates and assistance to homeowners and multi-family property owners for energy-efficient home improvements.
- Partner Programs:
- PG&E’s Energy Savings Assistance Program: Provides no-cost energy audits and technical assistance.
- GRID Alternatives: Provides job trainings and no-cost solar installations for low-income households.
- Rebuilding Together Peninsula: Provides home renovation and repair services for vulnerable residents.
Blog # 23
Climate Change
Researchers have examined the pathways in which increased temperatures can impact
health and generally recognize three main pathways: direct exposures, indirect exposures, and socioeconomic disruption. Extreme Weather-Related Injury, Displacement, and Mental Health Extreme weather events (storms, flooding) cause fatal and nonfatal injuries from drowning, being struck by objects, fire, explosions, electrocution, or exposure to toxic materials. A widespread weather related natural disaster may destroy or ruin housing, schools and businesses and cause temporary or permanent displacement. Individuals and families may experience post-traumatic stress, depression, and increased risk of suicide.
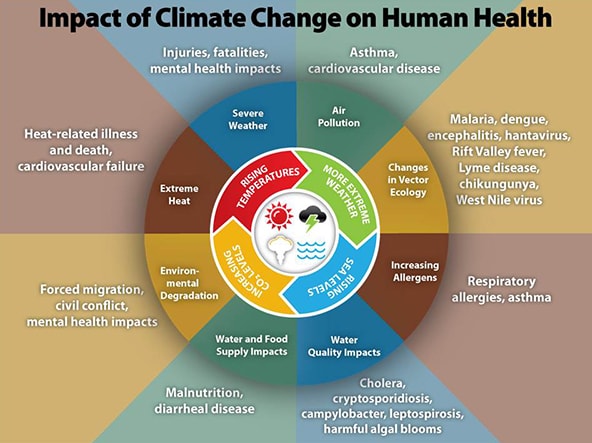
There is a broad range of environmental hazards attributed to climate change including heat waves, wildfires and wildfire smoke, air pollution, sea level rise and inland flooding in San Mateo County. In 2010, approximately 5% (34,798 residents) of the county’s population lived in fire hazard zones of moderate to very high severity. Climate change affects the social and environmental drivers of health outcomes. The effects of climate change can exacerbate existing health conditions and compound the risks of adverse health outcomes. The age adjusted death rate, which takes into account the effect of the population’s age distribution, is a basic indicator of the health status of communities. In 2010, the age adjusted death rate in San Mateo County was lower than the state average. Disparities in death rates among race/ethnicity groups highlight how certain populations disproportionately experience health impacts. Within the county, the highest death rate occurred among Pacific Islanders and the lowest death rate occurred among Asians.
In 2010, San Mateo County had approximately 17,223 outdoor workers whose occupation increased their risk of heat illness. In 2010, roughly six percent of households did not own a vehicle that could be used for evacuation (statewide average was 8%).
Natural disasters worsened by climate change increase the displacement of victims, which in turn increase population densities and tensions over resources.Violent crime also increases during heat events. In 2010, San Mateo County experienced approximately 2 violent crimes per 1,000 residents (statewide rate was 4 per 1,000 residents).
Nurses can make a powerful contribution to both mitigate climate change and to support people and communities around the world to adapt to its impacts. Leadership from nurses to take immediate action to build climate resilient health systems is necessary. This includes, but is not limited to, developing models of care to reduce unnecessary travel, developing climate-informed health programs for emerging infectious and communicable diseases; engaging in sustainable practices in the health sector, building the response capacity of the health workforce; engaging in health and climate research, and participating in intersectoral policy and governance responses.
- Work to enable nursing leadership and nurses to support healthcare organisations to contribute to climate change mitigation through implementation of environmental policies and sustainable practices.
- Engage in national and multisectoral measures to mitigate the impact of climate change on the population with a focus on vulnerable groups and those more exposed to disease and injury.
- Be involved in developing national action plans and policies for mitigation, adaptation, and resilience strategies as well as contribute to environmental health and justice policy making.
- Raise awareness of the health implications of climate change and how to assess and address climate change risks to health by developing policy documents on the subject.
- Embed the concept of sustainability in nursing practice as well as climate change-related knowledge into nursing curricula and in post-registration continuing education.
- Collaborate with other health professional organisations, intergovernmental organisations, environmental and health organisations and other civil society groups when developing health-adaptation policies and programs.
- Engage with media to promote public awareness of the harmful effects of climate change on health and to promote mitigation strategies
- Support the introduction of incentives for nurses to incorporate environmentally responsible health practices into their interventions.
- Strengthen existing and create new partnerships with humanitarian organisations and other national nurses’ associations (NNAs) to increase collaborative action.
- Advocate for policies that promote the reduction of healthcare waste and ensure correct waste management
- Actively engage in environmental health committees and policy-making that focus on the safety and protection of health workers and the management and regulation of the healthcare environment.
- Empower individuals, families and communities to make healthy lifestyle choices and change own practices (i.e. active transportation, use green energy, dietary changes) to decrease the contribution to greenhouse gases (GHGs).
- Engage with other sectors to support strategies that lower GHGs such as urban redesign, enhanced public transportation and modifying indoor technologies (i.e. cook stoves) to reduce emissions.
- Work with communities to build resilience to the impacts of climate change in a way that is driven by the local context and needs and that goes beyond reactivity but seeks to address underlying vulnerabilities. Strategies include vulnerability assessments to develop resilience plans, incorporating uncertainty in resilience planning, including poor and socially excluded groups into decision making, scaling successful adaption interventions, and monitoring and evaluation.
NEWS
PG&E to California: We need higher rates and profits to cope with wildfire risk
PG&E asked California regulators Monday for a hefty increase in rates and profits, raising average customer bills by more than $20 a month, saying the hike is needed to attract investment capital and deal with wildfire safety as the utility struggles in bankruptcy.
Along with an earlier rate increase proposed in December, PG&E’s new request would increase average household bills by $22.67 a month for electricity and natural gas, beginning in January 2020.
PG&E and California’s other major utilities, Southern California Edison and San Diego Gas & Electric, asked the Public Utilities Commission for fatter profit margins, seeing they need to offer investors a much higher return to compensate for the financial perils of major wildfires. The requests, which must be made every three years, come as Gov. Gavin Newsom and other state officials wrestle with PG&E’s bankruptcy and the financial health of utilities generally.
Utilities rarely get everything they want when they ask regulators for higher rates, and Monday’s request by PG&E in particular is almost certain to provoke a strong backlash from lawmakers in light of PG&E’s unpopularity over the deadly wildfires of 2017 and 2018. As it is, SB 549 by state Sen. Jerry Hill, D-San Mateo, would give the Legislature a say in authorizing rate increases for PG&E.
Blog # 22
Waste
Nurses can suggest or educate the following practices for food waste reduction;
- Implement tray-less dining in the hospital cafeteria to encourage customers to take only what they know they will eat.
- Cook made to order patient meals to help reduce the amount of food waste returned on patient trays.
- Repurpose left over food from one meal service to the next when possible.
- Utilize first-in first-out sticker systems to note which items should be used first.
- Track (manually or electronically) preparation and overproduction wastes for a simple and inexpensive way of gaining insight into opportunities to reduce food waste.
- Pilot food waste collection and diversion in the area of the hospital that generates the most food waste first (typically the main production kitchen), before rolling out to other food prep and service areas.
- Eliminate disposable plate and silverware in the cafeteria to make it much easier for customers to source separate their food scraps before leaving the cafeteria.
Nurses can protect staff by educating and training them about the importance of properly
managing and disposing of pharmaceutical waste, how to handle them and protect themselves. Nurses are responsible for ensuring that patients receive safe and effective medical treatment, they must also ensure safe and proper management and disposal of pharmaceutical waste. Acquiring the expertise and technologies necessary to properly manage and dispose of pharmaceutical waste can help protect employees, and the environment.

- To live zero waste life, I will make the following changes in my life;
- Use glass and stainless-steel containers that can be cleaned and reused over and over again.
- Set up a counter top Compost bin and put food waste into compostable trash bags, which can be turned in to municipal compost centers.
- Start using big shopping bags made from canvas, mesh, cloth or recycled/recyclable plastic.
- Prepare my lunch in a reusable lunch box.
- Use metal or glass water bottles throughout the day for water or coffee.
- Keep food and kitchen scraps, garden waste, and recyclables separate.
- Recycle all unbroken glass, some plastics, paper and cardboard, tin and aluminium cans.
Blog # 21
Occupational Health
The following image as emergency procedures hazard identification is available in my workplace. It provides a general information about different hazards and how to protect ourselves with clear signs. In my point of view, the signs and information are clear, simple and understandable to all levels of educations.

Reading and working with computer for several hours are my main safety issues which cause ergonomic hazards such as neck, shoulder, and back aching due to wrong posture. To reduce the spasm and pain, I do exercise and resting.
Blog # 20
Regulations & Policies
A state fish advisory issued today for Whiskeytown Lake in Shasta County provides safe eating advice for black bass species, Brook Trout, Sacramento Pikeminnow, Sacramento Sucker, and sunfish species.
Mar 12, 2019, Program: Fish
Guide to Eating Fish from San Francisco Bay
Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings to Californians about significant exposures to chemicals that cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. These chemicals can be in the products that Californians purchase, in their homes or workplaces, or that are released into the environment. By requiring that this information be provided, Proposition 65 enables Californians to make informed decisions about their exposures to these chemicals.
Proposition 65 also prohibits California businesses from knowingly discharging significant amounts of listed chemicals into sources of drinking water.
Proposition 65 requires California to publish a list of chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. This list, which must be updated at least once a year, has grown to include approximately 900 chemicals since it was first published in 1987.
Proposition 65 became law in November 1986, when California voters approved it by a 63-37 percent margin. The official name of Proposition 65 is the Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986.
The Attorney General has a special role in protecting the environment and public health in California. By law, the Attorney General has independent authority, acting directly in the name of the People, "to act to protect the natural resources of the State of California from pollution, impairment, or destruction." The Attorney General plays a leading role in the oversight and enforcement of two of California’s premier environmental laws—the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA), and the Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986 (Proposition 65). I personally track above policy through local or California news, and San Mateo county website because eating safe fish is important to me and my family. I have read several news about fish poisoning and learned neither type of fish poisoning can be detected by taste or appearance or prevented by cooking or freezing the fish.
Voluntary involvement in San Mateo county environmental health department's activities such as educate the public, participating in the meetings, discuss about the local environmental issues and proposing effective alternatives could promote local environmental health policies.
NEWS
Apr 03, 2019
Why is it taking so long to regulate toxic PFAS chemicals in Pennsylvania’s drinking water?
NEWS
Mar 20, 2019
Spinach, strawberries and kale top annual report on the most pesticide-tainted produceEvery year EWG analyzes the most recent USDA data (the agency doesn't test every kind of produce every year) on the most popular fruits and vegetables, which include more than 40,000 samples.
This year's "Dirty Dozen" — starting with the most polluted:
The entire "Clean Fifteen" list:
This list is helpful for people that cannot get organic versions of the dirty dozen, as it offers healthy produce that consistently tests clean.
Blog # 19 Sanitation - Basic Public Health
The County does not operate sewage treatment facilities. Sewage flows from the collection systems in County districts to sewage treatment plants operated by the South Bayside System Authority, or the cities of Burlingame or San Mateo. The County Sewer/Sanitation Districts pay the plant or city that treats the sewage.
The Grand Jury sought to determine whether the multiplicity of agencies focused on sewage collection and treatment is efficient and beneficial for San Mateo County residents. Its conclusion is that it is emphatically not. San Mateo’s cottage industry of sanitary districts fails in three important ways—public accountability, fiscal responsibility, and operational competence.
I believe Namma Toilet model which has been initiated by the government in the south of India can be an effective solution for people of India living in other states. Their public toilet blocks around the capital, Chennai, are designed for low-literacy users and entirely leapfrog the lack of existing sanitation infrastructure (sewerage lines). It’s a model that goes on to offer a liberating user experience that potentially changes behavior in a systemic fashion. |
Blog # 18
Pesticides
Low levels of pesticide residues may still remain on some foods, even organic foods. I choose to serve pesticide-free or organic produce at home or I can reduce pesticide residues on my food by;
To protect public health, regular monitoring of residues in food and the environment is required by setting maximum limits for pesticide residues in food and water. For example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) monitors and enforces pesticide tolerances (the maximum amount of pesticide residue that can legally remain in or on a particular food) in raw agricultural commodities and processed foods. Tolerances for meat, poultry and some egg products are monitored and enforced by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Pesticides on playing fields are considered a serious health concern. In this situation, I would keep my child out of treated areas until areas are dry. I would be sure my kid wash her hands before eating, especially after playing outdoors.
It is imperative to be familiar with the signs and symptoms of pesticides. The symptoms of pesticide poisoning can be broadly defined as either topical or systemic, can range from a mild skin irritation, vomiting, nausea, headache, weakness, dizziness, sweating, pin-point pupils, coma or even death. Prompt action during pesticide overexposure can prevent serious consequences, for example, identify the pesticide to which the victim was exposed, read the pesticide label information that will be useful in assisting a pesticide poisoning victim, and follow medical treatment procedures are listed on the product label.
|
NEWS
Mar 22, 2019 Weed killer residues found in 98 percent of Canadian honey samplesGlyphosate is the world's most widely used herbicide and is the active ingredient in Roundup brands as well as hundreds of others sold around the world for agriculture and other purposes. Use has grown dramatically over the last 25 years and consumers have become concerned about residues of the herbicide in their food. The data provides fresh evidence that glyphosate herbicides are so pervasive in the environment that residues can be found even in a food that is not produced by farmers using glyphosate. The researchers noted in their report that they ran into delays trying to calibrate their testing equipment "due to difficulties encountered in obtaining a honey sample which did not contain traces of glyphosate." Bees pick up traces of pesticides as they move from plant to plant, unintentionally transferring residues from crops or weeds sprayed with glyphosate back to their hives.  The Canadian report, published in a journal called Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, said that glyphosate is currently an active ingredient in 181 herbicides registered for use in Canada and its widespread use has made it commonly found in the environment. The study authors pointed out that Canada, like the United States, does not have a legal standard for how much of the herbicide is considered safe in honey. Regulators in different countries set what are referred to as "maximum residue limits" (MRLs) and tell consumers their food is safe if pesticide residues remain below the MRLs. In Europe, the MRL for glyphosate in honey is 0.05 mg/kg, also expressed as 50 μg/kg. The Canadian study authors said that all of the levels they found were below the European limit, though the highest was just barely within the legal limit. Because the residues did not exceed the MRL, they said, "the risk to consumer health appears to be quite low based on the residues detected." Several of the residue levels found by the FDA scientist in U.S. honey were above that so-called safe level that applies in the European Union. But the FDA, like the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and EPA, assert that as long as pesticide residues are below the legal MRLs, they are not harmful. Many scientists do not agree that MRLs actually are protective of public health, however. Blog # 17 AGRICULTURE: Food Safety
There are certain labels and ingredients to look for to ensure our food does not contain genetically modified organisms, artificial ingredients, and potentially harmful preservatives and additives. Food labels are an important source of information about calories and the nutritional value of the foods you eat, a crucial tool in building a heart-healthy diet.
I ate Mushroom Fettuccine today, bought from Trader Joe's. The ingredients are as following;
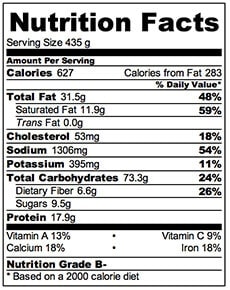 It was made in Monorovia, CA. The vulnerable populations I work with are older adults.
Overuse of antibiotics in agricultural is contributing to the emerging crisis of antibiotic resistance. Nurses can play a critical role in educating the public and policymakers on the importance of maintaining the efficacy of antibiotics by reducing overuse of antibiotics in agriculture. Antibiotics are extensively used in agriculture, primarily as feed additives for non-therapeutic purposes including growth promotion and routine prophylaxis, and many of these antibiotics are within classes also used in human medicine. When properly used, antibiotics are essential for treating infections in animals, but excessive and inappropriate use of the drugs is a problem. Reduce antibiotic use in food production to an agreed level in livestock and fish, along with restrictions on the use of antibiotics in these animals are important for humans.
Blog # 16
AGRICULTURE: Food Systems and FarmworkersHospitals are part of large contracted buying groups called group purchasing organizations (GPOs). Through GPOs, hospitals purchase everything from hospital equipment to food. Hospitals may have to buy a certain percentage—as high as 80-90 %—of their food through distributors from their GPO. Therefore, it is not always enough for a hospital to request a local and sustainable food item, since the particular product may or may not be available on contract. For these reasons, hospitals’ efforts to purchase sustainable food represent significant efforts to change institutional policies and practices, as well as the wider healthcare food service industry.
I might get information in our health care setting to know how and where they purchase the food and if those are healthy and sustainable food or not. I could introduce local organic farmers or/and connect my health care facility to those organic food producers to start a contract to buy and prepare healthy foods for the patients.
There is no factory farm in San Mateo. The nearest are located in Santa Cruz and Marin counties. However, I purchase the fruits and vegetables from local farmer markets which are organic and also planting %10 of the needed vegetables in our small garden without using pesticides.
 |
Blog # 15
Drinking Water
State Water Board (Drinking Water Division) oversees large water systems that provide drinking water for most of the public. This includes water systems that serve 15 or more service connections or 25 people daily for at least 60 days out of the year.
San Mateo County Environmental Health regulates smaller systems under the State Small Water Systems Program. A State Small Water System is a system that serves water to 5 to 14 service connections and fewer than 25 people daily for at least 60 days out of a year. These systems are usually found in rural areas. Environmental Health ensures that State Small Water Systems provide safe drinking water in adequate supply and under adequate pressure.
Environmental Health staff enforce the California Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA), which regulates water quality, maintenance, and systems design.
California Water Service - San Mateo
Environmental Working Group's (EWG) drinking water quality report shows results of tests conducted by the water utility and provided to the Environmental Working Group by the California State Water Resources Control Board, as well as information from the U.S. EPA Enforcement and Compliance History database (ECHO). For the latest quarter assessed by the EPA (July 2017 - September 2017), tap water provided by this water utility was in compliance with federal health-based drinking water standards.
Although global warming may bring some localized benefits, such as fewer winter deaths in temperate climates and increased food production in certain areas, the overall health effects of a changing climate are likely to be overwhelmingly negative. Climate change affects social and environmental determinants of health – clean air, safe drinking water, sufficient food and secure shelter.
Increasingly variable rainfall patterns are likely to affect the supply of fresh water. A lack of safe water can compromise hygiene and increase the risk of diarrheal disease, which kills over 500 000 children aged under 5 years, every year. In extreme cases, water scarcity leads to drought and famine. By the late 21st century, climate change is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of drought at regional and global scale.
Floods are also increasing in frequency and intensity, and the frequency and intensity of extreme precipitation is expected to continue to increase throughout the current century. Floods contaminate freshwater supplies, heighten the risk of water-borne diseases, and create breeding grounds for disease-carrying insects such as mosquitoes. They also cause drownings and physical injuries, damage homes and disrupt the supply of medical and health services.

If I were to develop a nationwide campaign to get people to drink tap water instead of bottled water, the slogan of my campaign would be "give away water bottles".
NEWS
Schoolchildren around the world are on climate strike. Here’s what you need to know.

Swedish climate activist Greta Thunberg holds a sign reading, “School strike for the climate,” as she attends a rally in Hamburg on March 1. (Daniel Reinhardt/DPA/AP)
On Friday, children in some 100 countries are walking out of school to push for global action on climate change. Over the past four months, hundreds of thousands of young people from many countries participated in demonstrations against climate change. This is something quite unique — schoolchildren have never before instigated such far-reaching protests on a global scale.
The phenomenon ramped up with weekly school strikes, mainly in Western Europe, the United States and Australia, but also in low- and middle-income countries like Colombia, India and Uganda.
In September, a 15-year-old Swedish student named Greta Thunberg launched a climate change strike in front of the Swedish parliament building just before the national elections. Greta soon became a source of inspiration for strike participants worldwide and has just been nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize.
A number of world leaders have invited Greta to sit down and talk. This move may suggest that the student-led climate movement has achieved the first necessary stage toward success — acceptance by its targets. Media coverage of Friday’s protests worldwide may also fuel further activism, involving schoolchildren as well as adults.
Nonetheless, the climate-striking schoolchildren have gotten a crash course in activism and mobilization — and may emerge as the next generation of activists committed to mass mobilization against the threat of climate change.




